Class 11th science physics(work power and energy)
Work, power, and energy are among the most important concepts of mechanics. A moving car, walking up stairs, lifting heavy objects, an airplane flying, etc are among the most common examples that give us insight into the concept of work, power, and energy. There are few common notions of work, power, and energy that can be precisely defined in physics. These notions and measurements can be utilized to define and predict the motion and behavior of bodies.
What is Work?
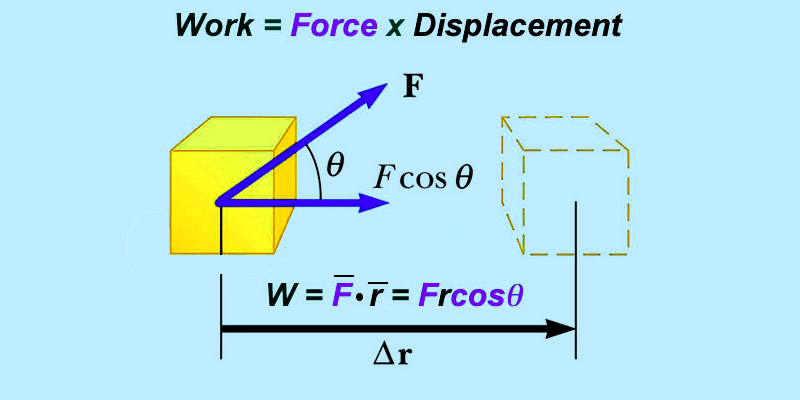
Work is the measurement of energy transfer that takes place when an object is displaced by an external force applied in the direction of the displacement.
What is Power?
The rate of doing work is called power.
What is Energy?
The capacity for doing work is called Energy. It may exist in kinetic, potential, thermal, chemical, electrical, nuclear, or various other forms. The SI unit of energy is the same as that of work.
What is the Principle of Conservation of Energy?
The Principle related to the conservation of mechanical energy states that the total mechanical energy of a substance remains in equilibrium if the only forces acting upon the body are conservative in nature.
Work Energy And Power Important Questions
- The sign of work done by a force on a body is important to understand. State carefully if the following quantities are positive or negative:
- (a) work done by a man in lifting a bucket out of a well by means of a rope tied to the bucket.
- (b) work done by gravitational force in the above case,
- (c) work done by friction on a body sliding down an inclined plane,
- (d) work done by an applied force on a body moving on a rough horizontal plane with uniform velocity,
- (e) work done by the resistive force of air on a vibrating pendulum in bringing it to rest.
- Underline the correct alternative :
- (a) When a conservative force does positive work on a body, the potential energy of the body increases/decreases/remains unaltered.
- (b) Work done by a body against friction always results in a loss of its kinetic/potential energy.
- (c) The rate of change of total momentum of a many-particle system is proportional to the external force/sum of the internal forces on the system.
- (d) In an inelastic collision of two bodies, the quantities which do not change after the collision is the total kinetic energy/total linear momentum/total energy of the system of two bodies.
The students can prepare all the important concepts included in this unit by referring to the work energy and power class 11 notes pdf from the links mentioned below:
- Work
- Energy
- Work
- Types of Energy
- Heat Energy and Internal Energy
- Different Forms Of Energy
- Power
- Conventional and Non-conventional Energy Sources
- Kinetic Energy
- Electric Power
- Potential energy
- Work and energy
 An individual goes to his workplace by walk, sits down at his desk from 10 a.m to 5 p.m does his work and at the end of the day returns to his home by walking. Is that so that work is done conferring to physics? He actually does no work as sitting in his office as it involves no displacement. He does work only for the duration of his walk to his office and back to home. This is what Physics states!
An individual goes to his workplace by walk, sits down at his desk from 10 a.m to 5 p.m does his work and at the end of the day returns to his home by walking. Is that so that work is done conferring to physics? He actually does no work as sitting in his office as it involves no displacement. He does work only for the duration of his walk to his office and back to home. This is what Physics states!
Work is believed to be done by a force when an object experiences displacement parallel to the line of action of the force. It’s an activity that includes force and movement in the direction of force. The capability for doing work is what the energy is! Let’s learn more about this.Principle of Work and EnergyThe work-energy principle says that the change in kinetic energy of a body is equivalent to the net work done on the body. This information is referred to as work-energy principle and is derivable from the conservation of energy.Here K.Ef is final kinetic energy and K.Ei is initial kinetic energy.Work and Energy EquationsIt is the resultant of the force applied (F) and the amount of displacement (d) and is articulated by equationW = F.dPower describes the rate at which work is done. It is articulated asThe energy or work is articulated in Newton-meter (Nm) or Joules or kgm2/s2 . 1 Joule is defined as the amount of heat released when a force of 1 newton acts over one meter of distance.Work vs. EnergyWork refers to overpowering resistance by the application of force. It is evident that the resistance has been overpowered from the movement of application of force. Energy is the capability to do work or perform some action and can be thought of something that is possessed or stored. It exists in several forms like light, heat, electrical, potential energy or other forms.Work and energy have similar units and are closely related. Energy can be put in storage, but that cannot be done for work. Work is energy in motion. Energy alters from one form to another by the process of doing work.Usually, there are two sorts of work Positive and negative work. If the direction of the force is in the same direction as the motion of its spot of application, work done is said to be positive.If the course of the force is in the opposite direction to the motion of its point of application, negative work is said to be done.
Comments
Post a Comment