Class 11th science physics(thermodynamics)
What is Thermodynamics?
Thermodynamics is concerned with the relationship between other forms of energy and heat. It explains how thermal energy is converted from other forms of energy. The energy coming from heat is termed thermal energy. When the tiny particles within an object move, they generate heat, more amount of heat is generated, when these particles move at a faster pace.
What are the Laws of Thermodynamics?
The laws of thermodynamics define the fundamental physical quantities like energy, temperature, and entropy that characterize thermodynamic systems at thermal equilibrium. The four laws of thermodynamics are:
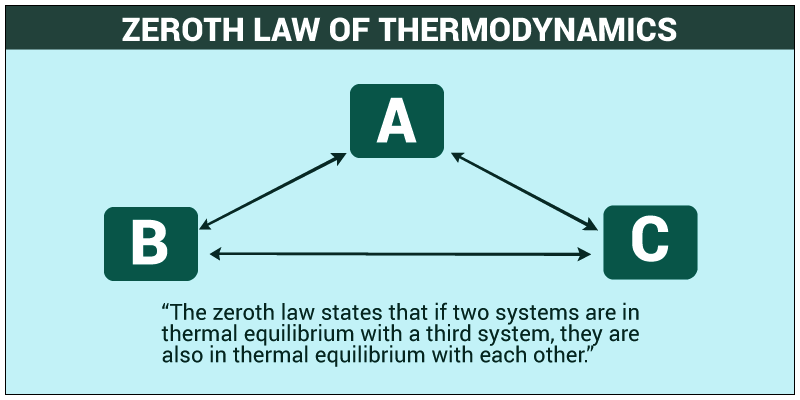
- Zeroth Law: It states that when two systems are in thermal equilibrium with the third system which is separate, the whole system together is said to be in equilibrium with one another.
- First Law: It states the law of conservation of energy when applied to a system in which the energy transfer occurs from or towards the system (with the help of heat and work). It represents the relation between the work done by the system, heat supplied to the system and the change in the internal energy of the system.
- Second Law: It states that it is not possible to find a system, where the absorption of heat from the reservoir is the complete conversion of heat into work.
- Third Law: This law states that at an absolute zero temperature, the system posses minimum energy.
What is Enthalpy?
In a thermodynamic setup, enthalpy is the measurement of energy. The quantity of enthalpy equals the total content of the heat of a system, equivalent to the system’s internal energy plus the product of volume and pressure.
Numerically, H (the enthalpy), equals the sum of E (the internal energy), and P (the product of the pressure), and V (volume) of the system.
H = E + PV
What is Entropy?
Entropy’s value depends on the physical state or condition of a system. It is a thermodynamic function used to measure the randomness or disorder of a system. For example, the entropy of a solid, where the particles are not free to move, is less than the entropy of a gas, where the particles will fill the container.
We already know that heat is a form of energy. It is a common observation that when we come out of the blanket on a cold morning we feel cold for some time but after that, it becomes normal to some extent. So what exactly is happening? Initially, heat begins from us to the surrounding and thus we feel cold. So till when heat will flow from us to surrounding? To answer this we introduce something known as temperature. It is basically the measure of hotness or coldness of a body. Heat exchange takes place between two bodies till their temperatures become equal. Also, it flows from a body at a higher temperature to one at a lower temperature.
Thermal Equilibrium
So now that we know about temperature we are in a position to define thermal equilibrium. It is defined as a situation in which no heat flows from one body to another when brought in contact with each another. In a broader sense when the parameters of the system like volume, pressure, temperature, or composition does not change. As heat does not flow we can also say both bodies acquire the same temperature at equilibrium.
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
One of the laws related to the thermal equilibrium is Zeroth law of Thermodynamics. Suppose two bodies are separated by a heat insulator. Now a third body is brought in contact with both the bodies simultaneously. When the bodies attain thermal equilibrium we remove the third body. Now we can also remove the heat insulator and find no heat is transferred from one body to another.
According to Zeroth Law if two bodies I and II are in equilibrium with a body III separately then it follows that body I and body II are also in thermal equilibrium. As no heat flows from I to III hence, TI = TIII similarly TII = TIII. It follows that TI = TII, hence no heat flows.
To learn in details about all the laws of thermodynamics visit the links given below.
Applications of Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
The zeroth law of thermodynamics can be applied to compare temperatures of more than two objects. If the heat can pass through two objects without any external heating source, the two objects are said to be in thermal equilibrium. For instance, if the swimming pool you are in and your temperatures are similar, no heat flows from either sides apart from minute possibility. While, if you get into the pool cracking through the ice layer, you are not in the state of thermal equilibrium with the water. Please don’t try this experiment. To check for thermal equilibrium mainly in case of frozen pools, you should use a thermometer.
The zeroth law frames an idea of temperature as an indicator of thermal equilibrium. The two given objects are in a state of equilibrium with the third object that gives you the required reading on a scale.
Comments
Post a Comment