Class 11th science physics (oscillation)
What are Oscillations?
Oscillation is a measure of some repetitive variation, as a function of time. It can be measured with respect to a state of equilibrium. The most common and simplest example for oscillation is the motion of a simple pendulum.
What are the three main types of Simple Harmonic Motion?
The three main types of simple harmonic motion in physics are:
- Free Oscillation
- Forced Oscillation
- Damped Oscillations
Free Oscillation
In here, the amplitude and time period remains constant without any influence of external factors. When the system has zero damping, the amplitude remains constant provided, this theory is possible in cases where damping always occurs.
In order to overcome external forces like air resistance or friction, the reduction in amplitude(energy loss of a system) is referred to as damping. As a result, the amplitude, frequency, and energy all remain constant.
Forced Oscillation
When an external periodic force influences a body’s oscillation, then it is called forced oscillation. Here, damping occurs in the amplitude of oscillation but remains constant with the help of the external energy supplied by the system.
For example, constantly pushing a swing so that its oscillation doesn’t reduce.
Damped Oscillation
The reduction of the amplitude of an object with respect to time, such type of oscillations are known as damped oscillations. The energy of a system decreases with the decrease in amplitude. There are two types of damping:
- Natural Damping
- Artificial Damping
A sound is a form of energy that is produced by vibrating bodies. It requires a medium for the propagation. It cannot propagate in a vacuum as there will be no material to transfer sound waves. Sound cannot be produced without the vibration of objects. The back and forth motion of an object are known as sound vibration. This to and fro motion or back and forth motion is also known as oscillatory motion. The regular rhythmic back and forth movement are referred to as oscillation. Some of the quantities that are used to explain sound are period, frequency and amplitude. They are described below:
Period of sound
A period can be said to be the time taken to do something. If an event occurs repeatedly then the event is said to be periodic. The time taken by the periodic event to repeat itself is known as the period. The time taken by the particle to complete one vibration cycle is the time period for that particle.
Period = 1/Frequency
Frequency of Sound
The number of oscillations per second is known as the frequency of oscillation. Its unit is hertz and is denoted by Hz. The frequency of a wave in general means how frequently the particles of a medium vibrate when a wave moves through the medium.
Frequency = 1/Period
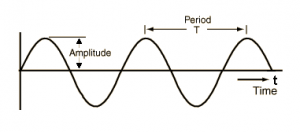
Amplitude of sound
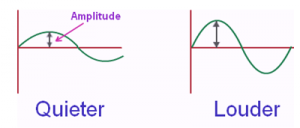
The amplitude of a sound wave is the measure of the height of the wave. The amplitude of a sound wave can be defined as the loudness or the amount of maximum displacement of vibrating particles of the medium from their mean position when the sound is produced. It is the distance between crest or trough and the mean position of the wave.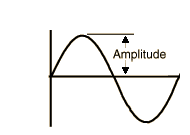

Loudness is directly proportional to the amplitude of the sound. If the amplitude of a sound wave is large then the loudness of sound will be more. If the amplitude is small then the sound will be feeble.
Comments
Post a Comment